Published 25 August 2023
Take Control of Your Hives: Know Your Triggers
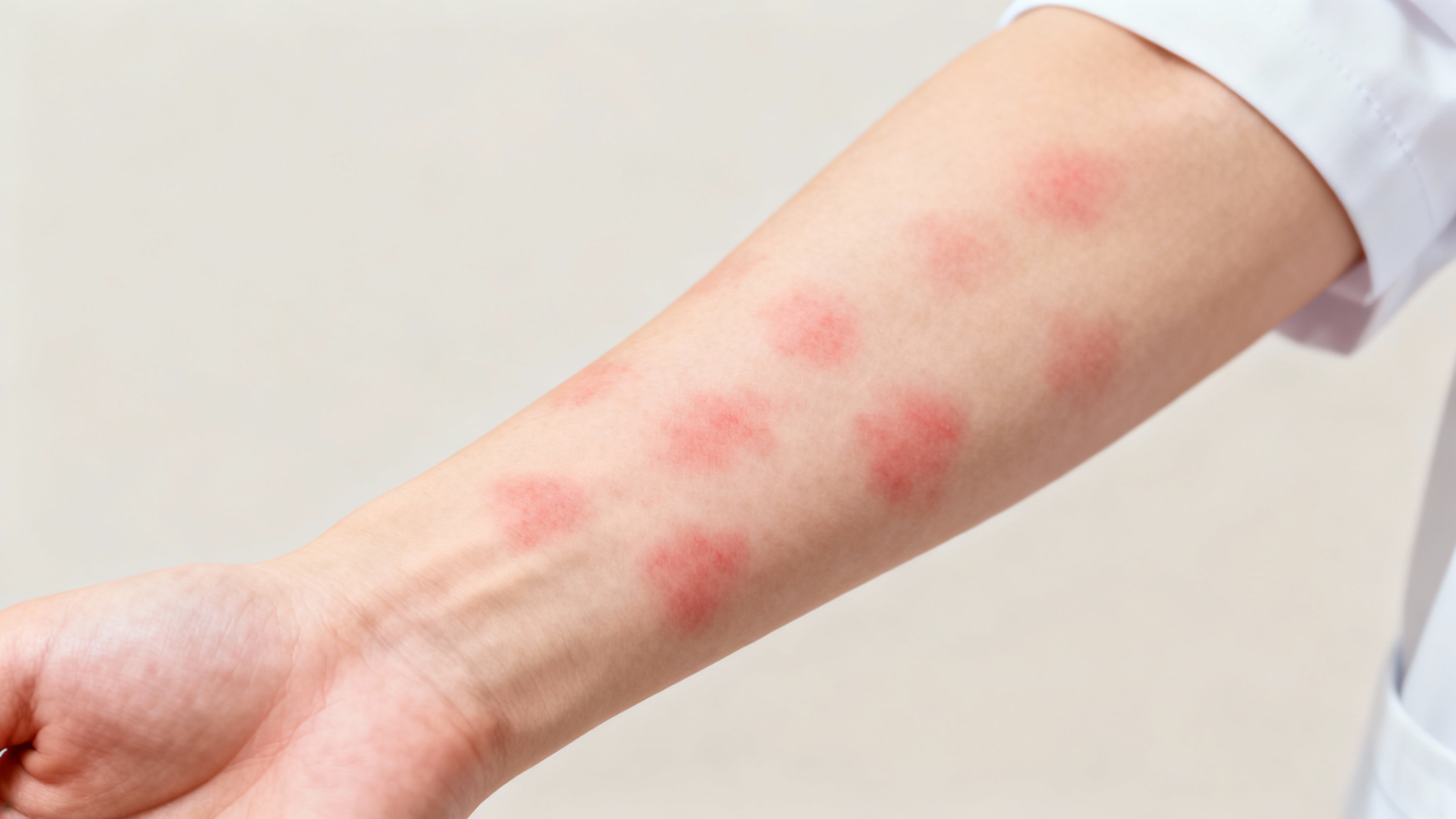
Understanding Hives
Hives, also known as urticaria, are a common skin condition characterized by itchy, raised welts on the skin. They can appear suddenly and vary in size and shape. Understanding the causes and triggers of hives is essential for effectively managing this condition.
What Are Hives?
Hives are a type of allergic reaction that occurs when the body releases histamine in response to an allergen or trigger. Histamine causes the blood vessels to leak fluid into the skin, resulting in the characteristic raised welts and itching associated with hives. These welts can appear anywhere on the body and may come and go within a few hours or persist for several days.
Causes and Triggers of Hives
Hives can be triggered by a variety of factors, including allergens, environmental triggers, food triggers, and medications. Common allergens that can cause hives include pollen, pet dander, and certain foods. Environmental triggers, such as heat, cold, or sunlight, can also lead to the development of hives. Additionally, certain foods, such as shellfish, nuts, and eggs, can trigger hives in susceptible individuals. It’s important to note that hives caused by food allergies are different from food intolerance, which may manifest with similar symptoms but involves a different immune response.
Medications, including antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and certain pain relievers, can also trigger hives in some individuals. In some cases, hives may even be triggered by underlying health conditions, such as viral infections or autoimmune disorders. Understanding your specific triggers can help you avoid or minimize exposure to these factors, reducing the likelihood of hives outbreaks. If you suspect that your hives may be related to a specific trigger, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate testing and diagnosis. To learn more about allergy testing for hives, visit our article on allergy testing for hives.
By understanding the nature of hives and the factors that contribute to their development, you can take proactive steps to manage and prevent hives outbreaks. Identifying your triggers, keeping a hives diary, and seeking medical advice are essential in effectively managing this condition. In the following sections, we will explore these topics in more detail and provide strategies for coping with hives symptoms.
Identifying Your Triggers
To effectively manage and control hives, it’s crucial to identify the triggers that can cause hives to flare up. Triggers can vary from person to person, but they generally fall into four main categories: common allergens, environmental triggers, food triggers, and medication triggers.
Common Allergens
Common allergens, such as pollen, pet dander, and dust mites, can trigger hives in susceptible individuals. These allergens can be inhaled or come into contact with the skin, leading to an allergic reaction that manifests as hives. If you suspect common allergens may be triggering your hives, it’s advisable to consult an allergist for allergy testing. They can help identify specific allergens and develop an appropriate treatment plan. For more information on allergy testing for hives, visit our article on allergy testing for hives.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors like extreme temperatures, humidity, and exposure to sunlight can also trigger hives in some individuals. For example, cold urticaria is a condition where exposure to cold temperatures leads to hives. Similarly, heat urticaria is characterized by hives that occur due to exposure to heat. If you suspect environmental triggers may be causing your hives, try to minimize exposure to extreme temperatures and protect your skin from direct sunlight. For more information on managing hives triggered by environmental factors, consult our article on managing hives symptoms.
Food Triggers
Certain foods can trigger hives in individuals with food allergies or intolerances. Common culprits include shellfish, nuts, eggs, and dairy products. If you suspect that certain foods may be triggering your hives, it’s essential to keep a food diary to track your symptoms. This can help identify patterns and narrow down potential food triggers. For more information on hives triggered by food allergies or intolerances, read our article on hives and food intolerance.
Medication Triggers
Certain medications, such as antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and ACE inhibitors, can trigger hives in some individuals. It’s important to be aware of any medications you are taking and to consult your healthcare provider if you suspect a medication may be causing your hives. They can provide guidance on alternative medications or adjust your treatment plan accordingly. For more information on hives triggered by medications, refer to our article on prescription medications for hives.
Identifying your specific triggers is a crucial step in effectively managing and controlling hives. Once you have identified your triggers, you can take proactive measures to avoid or minimize exposure to them. This may involve making lifestyle changes, seeking medical advice, or using appropriate medications. By understanding your triggers, you can gain better control over your hives and improve your quality of life.
Keeping a Hives Diary
The Importance of Tracking Triggers
When it comes to managing hives, understanding your individual triggers is crucial. Hives, also known as urticaria, can be triggered by a variety of factors, including common allergens, environmental triggers, food triggers, and medication triggers. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help prevent or minimize hives outbreaks.
To effectively identify your triggers, keeping a hives diary is highly recommended. A hives diary is a record of your daily activities, symptoms, and potential triggers. By tracking your experiences, you can start to identify patterns and potential triggers that may be causing your hives.
How to Keep a Hives Diary
Keeping a hives diary is a simple and effective way to track your symptoms and potential triggers. Here are some steps to help you get started:
-
Record your symptoms: Start by documenting the date and time when your hives appear, along with a description of the symptoms. Be sure to include details such as the location of the hives, the size, and any accompanying symptoms like itching or swelling.
-
Record your activities and exposures: Note down any activities or exposures that may have occurred shortly before the hives outbreak. This includes things like exposure to allergens, changes in environment, consumption of specific foods, or the use of new medications.
-
Include details about your surroundings: Take note of any changes in your environment, such as temperature, humidity, or exposure to potential triggers like pet dander or pollen. This can help you identify environmental triggers that may be contributing to your hives.
-
Track your diet: Keep a record of the foods you consume each day. This includes meals, snacks, and any new additions to your diet. By tracking your diet alongside your hives outbreaks, you may be able to identify specific foods that trigger your symptoms. For more information on the connection between hives and food, check out our article on hives and food intolerance.
-
Record medication use: If you are taking any medications, make sure to document them in your hives diary. This includes prescription medications, over-the-counter drugs, and supplements. Changes in medication can sometimes trigger hives, so it’s important to keep track of what you are taking.
-
Be consistent: To get the most accurate picture of your triggers, it’s important to be consistent in recording your experiences. Make it a habit to update your hives diary daily, noting any changes or new information that may be relevant.
By diligently keeping a hives diary, you can begin to identify patterns and potential triggers that cause your hives outbreaks. This valuable information can help you make necessary lifestyle changes, avoid triggers, and seek appropriate medical advice. For more information on managing hives and finding relief, take a look at our article on coping with hives and hives relief tips.
Managing and Avoiding Triggers
Managing and avoiding triggers is a crucial aspect of hives management. By minimizing exposure to allergens, making lifestyle changes, and seeking medical advice, individuals with hives can take control of their condition and reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
Minimizing Exposure to Allergens
One of the primary ways to manage hives is to minimize exposure to allergens that can trigger an outbreak. Common allergens that may contribute to hives include pollen, pet dander, dust mites, and mold. It’s important to identify these allergens and take steps to reduce your exposure to them. This may involve regularly cleaning your living space, using air purifiers, and taking precautions when spending time outdoors during high pollen seasons. For more information on managing seasonal allergies, refer to our article on hives and seasonal allergies.
Making Lifestyle Changes
Certain lifestyle changes can also help manage hives. Stress is known to trigger hives in some individuals, so practicing stress management techniques such as meditation or yoga can be beneficial. Additionally, avoiding hot water showers or baths and opting for lukewarm water can help prevent hives outbreaks. Some individuals find relief by wearing loose-fitting clothing made from natural fabrics, as synthetic materials can sometimes irritate the skin.
Seeking Medical Advice
While self-management strategies can be helpful, it’s important to seek medical advice if hives persist or worsen. A healthcare professional can conduct a thorough evaluation to identify the underlying cause of the hives and determine appropriate treatment options. They may recommend further allergy testing to pinpoint specific triggers or prescribe medications to alleviate symptoms. For more information on medical treatment options for hives, refer to our article on hives treatment options.
By actively managing and avoiding triggers, individuals with hives can significantly improve their quality of life and reduce the discomfort associated with outbreaks. However, it’s important to remember that each person’s experience with hives is unique, and what works for one individual may not work for another. It may take some trial and error to find the best strategies for managing your hives, so don’t hesitate to seek medical advice for personalized guidance and support.
Coping with Hives Symptoms
Experiencing hives can be uncomfortable and distressing, but there are ways to manage the symptoms and find relief. This section will focus on three key aspects of coping with hives: soothing the itch, reducing swelling and inflammation, and exploring over-the-counter relief options.
Soothing the Itch
The intense itch that often accompanies hives can be overwhelming. However, there are measures you can take to alleviate this discomfort.
- Cool compresses: Applying a cool compress or taking a cool bath can help soothe the itchiness and provide temporary relief.
- Moisturizers: Regularly moisturizing your skin with fragrance-free lotions or creams can help soothe dryness and reduce itching.
- Avoid hot water and harsh soaps: Hot water and harsh soaps can further irritate your skin and exacerbate the itch. Opt for lukewarm water and gentle, hypoallergenic cleansers.
Reducing Swelling and Inflammation
Managing the swelling and inflammation associated with hives is an important aspect of finding relief. Consider the following strategies:
- Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers that cause the hives outbreak can help minimize the swelling and inflammation. Keep a hives diary to track your symptoms and identify patterns.
- Applying cold compresses: Just like with soothing the itch, applying a cold compress can help reduce swelling and inflammation by constricting blood vessels.
- Elevating affected areas: If your hives are localized to certain areas, elevating those areas can help reduce swelling by promoting better circulation.
Over-the-Counter Relief Options
Over-the-counter medications can provide temporary relief from hives symptoms. These options include:
- Antihistamines: Antihistamines can help alleviate itching and reduce the severity of hives outbreaks. They work by blocking the release of histamine, a key player in allergic reactions. Consult with a healthcare professional or pharmacist to find the appropriate antihistamine for your needs.
- Topical creams and ointments: Over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams or calamine lotions may help reduce redness, itching, and inflammation. However, it’s important to follow the instructions and consult a healthcare professional if your symptoms persist or worsen.
- Oral pain relievers: In some cases, over-the-counter pain relievers like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be used to alleviate discomfort associated with hives. However, consult with a healthcare professional before taking any medication to ensure it is suitable for you.
It’s important to note that these over-the-counter options provide temporary relief and may not address the underlying cause of your hives. If your hives persist, worsen, or interfere with your daily life, it is recommended to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can help identify triggers, recommend appropriate treatment options, and provide guidance on managing your hives effectively.
Remember, finding relief from hives symptoms is a process of trial and error. What works for one person may not work for another. Be patient and persistent in your efforts to find the most effective coping strategies and relief options.
